By Jeri Rutherford, Food Scientist and Owner of RideOut Technologies
Over half of Americans (51%) say they want to lose weight *1. Weight loss is the number one New Year’s resolution. Personally, I don’t know anyone who wouldn’t prefer to be five pounds lighter. If this is such a common goal, why don’t we achieve it more often? Why is it so hard?
In a CDC report, Connie Diekman, Director of Nutrition University at Washington University in St. Louis stated: “Sustainable diet changes that includes cutting sugary, fat-laden junk food, and replacing it with plenty of fruits, vegetables, fiber-rich grains and other healthful whole foods is a start combined with regular exercise.” She also goes on to state that most people need a sustainable plan to be successful. For the most part we all know this, we all know we should eat healthy food, eat less and work out more. So let’s examine the physiology of shedding just five pounds to understand why sometimes we are not successful.
What Happens Inside the Cell
When we consume food, the carbohydrates, (starches, sugars, simple and complex carbohydrates) and fat are broken down into Glucose (blood sugar). Glucose is a relatively simple molecule that can be moved by your blood to all the cells in your body. Inside the cell, glucose is turned into acetyl CoA in the cell and then turned into ATP using the Krebs (or Citric Acid) cycle and metabolized, (burned). Inside the cell, ATP is turned into ATD and the primary byproducts are water, heat and CO2.
The CO2 is exhaled by the lungs, heat is released by the skin while the water is reused or sent to the kidneys.
Blood sugar has a pretty short shelf-life. It circulates in the blood stream and can be stored by your liver, but only for a maximum of 48 hours. If we have eaten more calories than we need at the time of consumption, that blood sugar is converted to fat or Adipose tissue. If we don’t have enough blood sugar to meet our needs, our body can make it by converting our fat and protein into glucose.
Consumed protein is broken down into amino acids which are compounds that play many critical roles in your body. Proteins cannot be synthesized and are needed for vital processes in our bodies like the building of proteins, muscles and synthesis of hormones and neurotransmitters. *2
Understanding that your body can make glucose from fat is critical because to lose overall body weight, we must consume less calories than we burn. We must make our bodies burn stored fat.
On a side note: a calorie is a unit of heat measurement. Foods, when “burned” release heat. Laboratories measure this heat and from that measurement our food calories are calculated. A calorie is nothing more than a convenient way to understand how much energy is stored inside a given food.
A pound of adipose tissue, body fat, will produce about 3300 calories when it is converted into blood sugar. If one wanted to lose five pounds that would be 16,500 calories, (kcal) that must be burnt by our activity. To help understand these numbers a bit more, a pound of butter has 3250 calories. When we shed a pound of body weight, that is equal to burning off a pound of butter. *3
Thankfully, we all burn calories every day, just to keep our bodies alive and going about our business. That is called our BMR, (Basal Metabolic Rate). The BMR for adults varies from 1700 to 2500 calories per day depending on your sex, age, current weight, fitness level and level of activities. Your BMR can be calculated here, *4 . Taking the time to calculate your BMR is helpful, it is good to understand that simply existing will use “X” number of calories. Now when we add activities onto our simple existence, we get a very good idea how many calories we are using in a day.
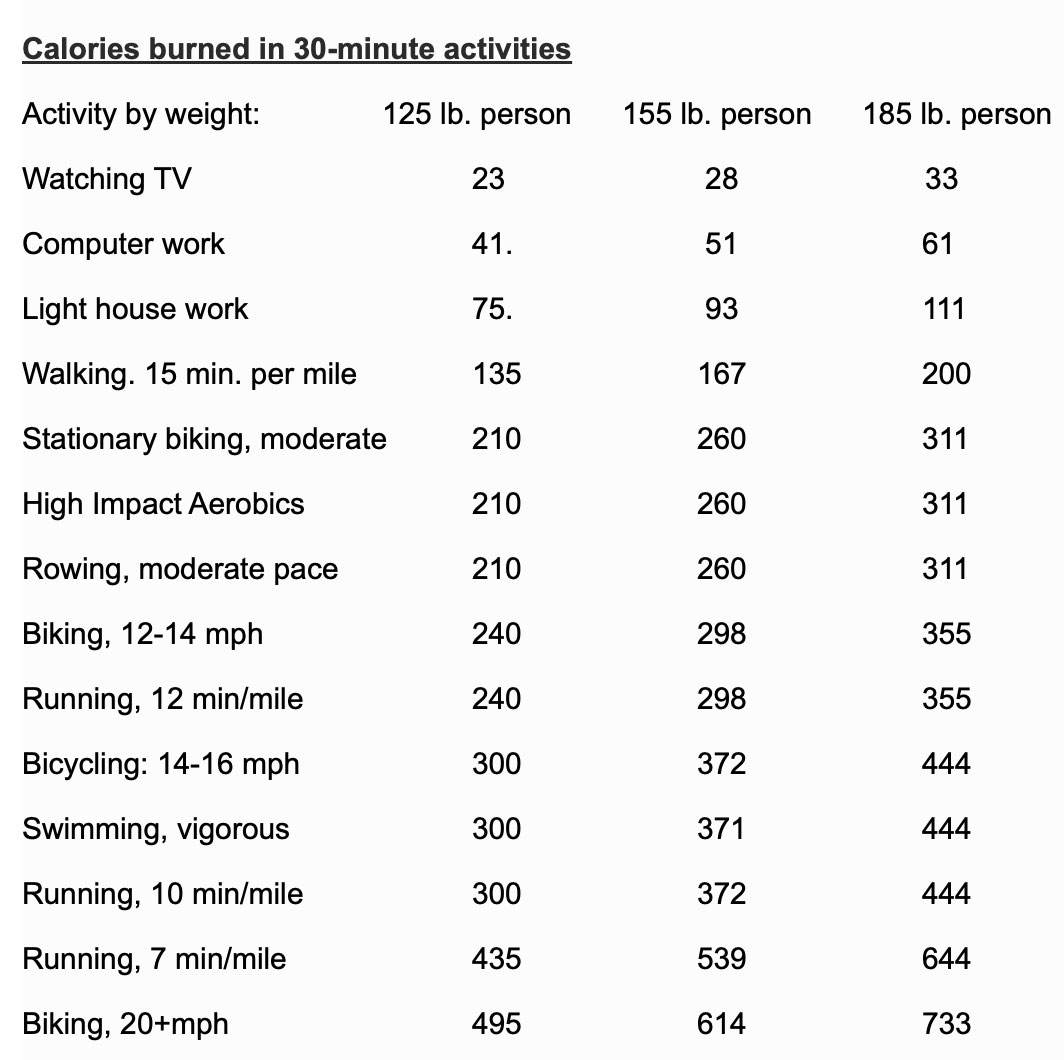
Look at the chart below created by Harvard Medical School *5 to understand the effect of activities on caloric burn.
Examining this chart, we see some activities such as high impact aerobics and running have very similar caloric consumption as fast biking. Many people, including this author, have switched from running and impact aerobics to biking due to knee pain. Also, some folks believe that biking is a “fountain of youth”, as we can get it all, the endorphins, the joy of the environment, the fresh air, fun, an ever-changing view that keeps us engaged, a non-jarring exercise that moves blood into our joints and the freedom given to us by a simple machine, the humble bike. For being engaged and enjoying exercise is the most important aspect of a consistent exercise routine. If you don’t enjoy the exercise activity, you simply will not do it for more than a few weeks.
High Intensity Interval Training and Bicycling
Lastly, biking, by its very nature can be a natural HIIT workout. HIIT or High Intensity Interval Training has been shown to be extremely effective for weight loss and overall body toning. While biking creating a HIIT workout can be as simple as mixing very fast bicycling for two minutes then active biking for three minutes and repeat this pattern five more times in a row without stopping. Another natural HIIT is to climb a hill as fast as you can, recover on the way down and repeat.

Furthermore, if you are not comfortable on your bike, if you don’t have a comfortable bike saddle, you will not be riding. The number one complaint people list for not riding their bike is seat discomfort. Your bike may cost $25 or $2500, yet the most important part is that you are comfortable on the seat. Biking should be fun. The more enjoyable and fun an activity is, the longer you will do it. Fun could be as simple as a evening ride or a blender of Margaritas attached to a bike.
Additional benefits from biking/exercise are explained by Stephen Graef, PhD, a sports psychologist at The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center who stated; “Exercising consistently over time will bring even more benefits that help mood, like reduced stress”. *6 It is widely understood that the endorphins released by the muscles during the fatigue stage have been shown to help regulate appetite.
Stress is the arch-enemy of weight loss. A contributor to stress is lack of sleep. A small study reported depriving nine men of sleep for a single night resulted in significant increases in hunger and levels of ghrelin, the hormone that stimulates appetite. On the other hand, a study in 245 women found that improving sleep quality and squeezing in at least seven hours of sleep each night increased the likelihood of successful weight loss by 33%. Almost counter intuitive, that more sleep aids weight loss. Yet the practical and applied application of this is that making yourself tired from a long bike ride means you and not feel as hungry and should sleep better which will help to reduce your hunger cravings long term.
A government study found the key to maintaining muscle tone in adults is exercising working out four to five days a week for longer periods of time without reaching extreme muscle fatigue. This again ties well with bicycling, as one can easily substitute driving to a location such as work or school instead of driving. Again, as mentioned in the first paragraph of this article, having a plan is key to success. For a plan to work long-term it must have fun and enjoyment as a part of it. Start today and create your plan!
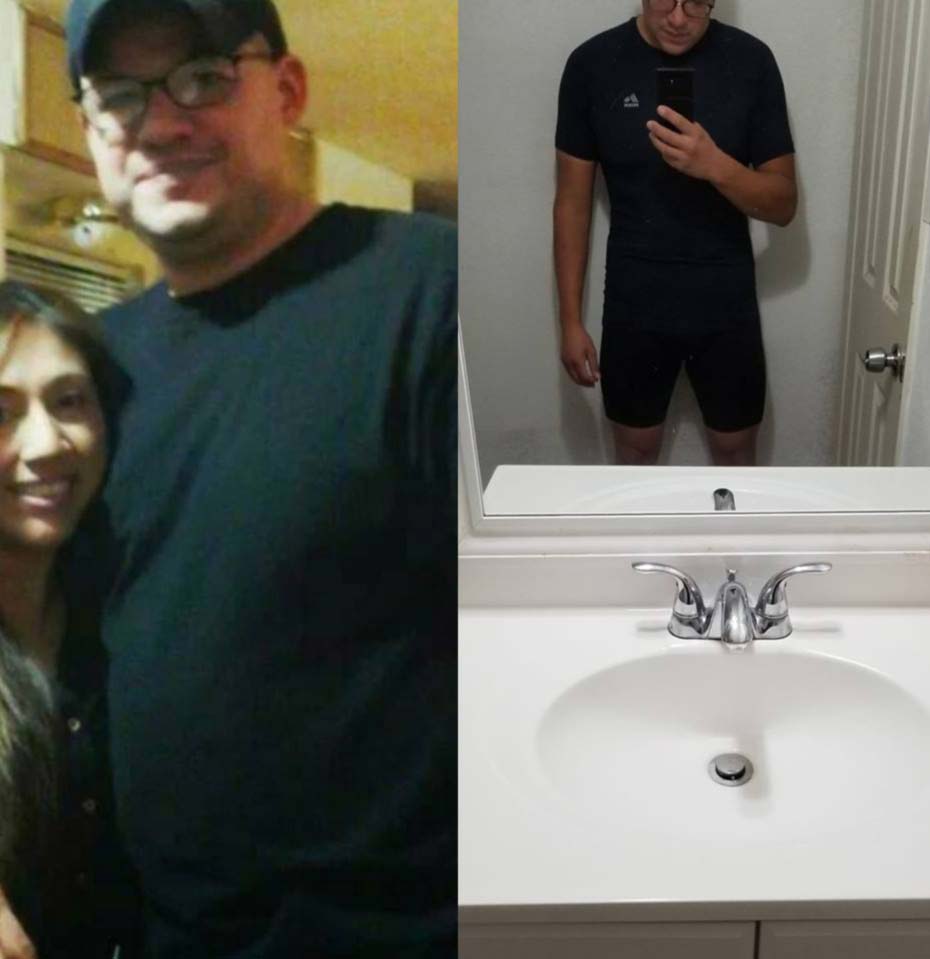
To help get you motivated, take a look at Hector’s results!
Contributed by Hector Perales
“I used to weigh 285 lbs., goal is 176 lbs.”

If you are looking for a seat for long distance riding, look no more! these comfortable mountain bike saddles and comfort seats will aid you in your firness goals.
seeking a comfy seat for ladies, try our Pink carbon Comfort. If you are looking for a bicycle seat for big guys, try the Storm Quest. Lastly is you are a lighter weight person searching for a comfortable road bike saddle, try the Green Carbon Comfort.

If you have a biking and weight loss story you would like to share or questions about how to make your bike seat more comfortable, please contact us at rideouttech.com.
Bibliography and Links
*1: https://www.webmd.com/diet/obesity/news/20180712/half-of-americans-trying-to-slim-down
*2: https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/essential-amino-acids
*3: https://www.forbes.com/sites/quora/2017/05/08/what-actually-happens-to-your-body-when-you-burn-a-calorie/#751f6cd2772b
*4: https://www.calculator.net/bmr-calculator.html
*5: https://www.health.harvard.edu/diet-and-weight-loss/calories-burned-in-30-minutes-of-leisure-and-routine-activities
*6: https://www.verywellfit.com/how-to-burn-more-fat-with-a-hiit-workout-3495991


3 comments
Great article-easily understood.
Thanks, Carole.
Good content, thanks